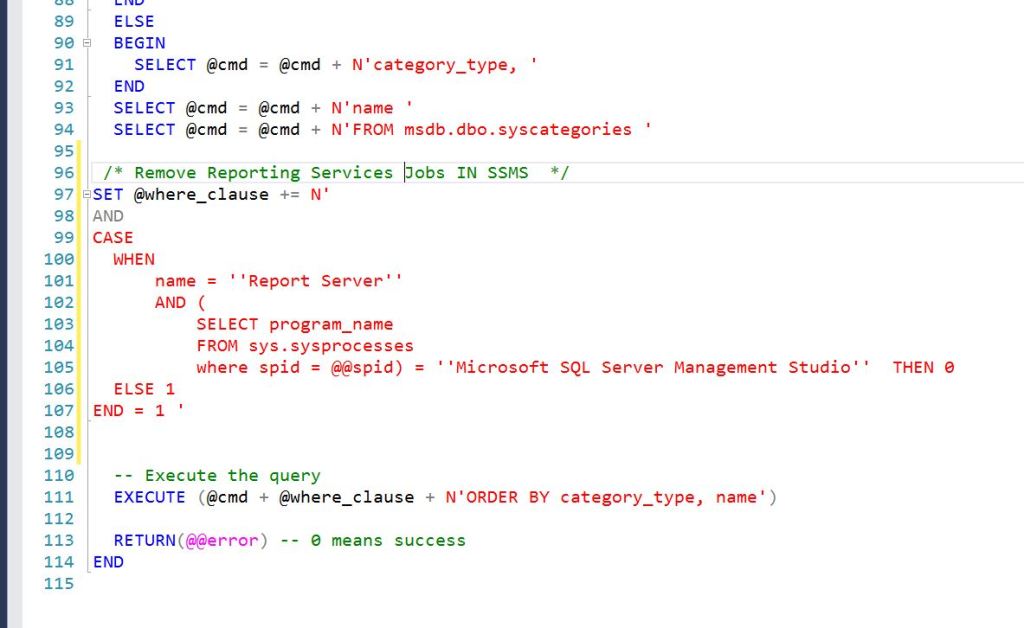
There are many reasons for terminating a long running SSIS Package. Sometimes someone accidentally kicks-off a monthly job instead of a daily job, or you just clicked the wrong item, either way SQL Server performance is affected. Whatever the reasons, you need to stop the job.
Read more: Terminate SSIS Jobs: A Step-by-Step GuideThe cleanest way I have found to stop a SSIS package is by first running the following query to identify the processes that you want to stop.
You can either use End_Time is null or Status = 2 in the where clause.
select execution_id,folder_name,project_name,status,start_time,end_time
from catalog.executions where end_time is null

This shows all of the SSIS jobs that SQL Serve thinks is still running. Some of these above are from 3-4 years ago, so I know they are not active.
Status of 2, indicates that SSIS still thinks that the process is running.
The other possible status results are (from the docs):
“created (1), running (2), canceled (3), failed (4), pending (5), ended unexpectedly (6),
succeeded (7), stopping (8), and completed (9).”
Now using the execution_id from the query above, we now need to use the catalog.stop_operation stored procedure to cancel the job:
exec catalog.stop_operation @operation_id=648469

After re-running the query, we can see that the job is no longer showing up as a running task.

Below I am stopping all of the jobs.

Rerunning the query now shows that no jobs are running.

For unknown reasons, sometimes the SSISDB database thinks old jobs are still running even though you do not see anything running. Now you have an easy way to stop/delete them.
For further reading, feel free to read these selections about: catalog.stop_operation and catalog.executions.